Today I’m going to show you how to utilize and ease your dev life with Firebase tool and the services it provides for Web, not Android nor iOS.
What Is Firebase?
Firebase is a technology that allows you to create web applications without server-side programming, making development faster and easier, its a platform that provides developers with tools and services to help them develop high-quality apps.
So why should you use Firebase as your web app platform?
Okay let me explain well, as you are progressing in your web development career, you tend to have more great ideas on the project but available with little or no resources to accomplish them.
Just imagine you trying to integrate a Serverless CMS into a project, all you’ve got is just HTML, CSS, JS, along with some Frameworks in your toolbelt, No SQL Skills.
And creating a custom server is a lot of pain for Frontend Developers, so how do you make that idea get to work out in real life?
But with platforms like Firebase:
- You don’t have to buy and manage servers, neither do you have to worry about downtime, Google manages that for you.
- Saves you time.
- You don’t have to start settling and querying databases e.g MySQL
- You don’t have to write all the backend code for the server.
- Your codebase stays smaller.
- Everything you need is integrated, so it solves the problems.
Firebase Services
Firebase services with in-depth coverage for Web.
- Firebase Hosting
- Firebase Realtime Database
- Firebase Analytics
- Firebase Storage
- Firebase Authentication
Let’s dive right in;
1# Firebase Hosting
So you are done writing your codes and you need to serve this static content, contents which include your HTML, JS, CSS files as well as images and other assets that your client-side app needs to run.
Well, Firebase has an integrated static file hosting solution which is very easy to use.
you deploy codes through your command line, you can roll back to your previous website version if your code gets broken, isn’t this cool?
not just this alone, Firebase allows you to add custom domain names, it automatically issue SSL certificate for you, so you are protected by HTTPS, you can redirect your URLs, rewrite URLs
So now let me walk you through getting all this done
Head on over to your Firebase console, and create a project. don’t worry, it’s free, no credit card required either.
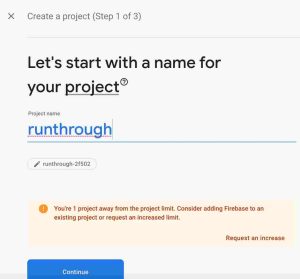

When you are done creating your project, the dashboard will look like this
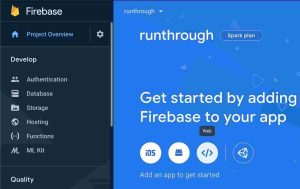
Now click on the web and set it up, put your web app name and click the drop-down in that also set up Firebase Hosting and pick your project.

Go to your project folder in VSC, where all your codes are, now open your integrated terminal or your system command line, now run the following commands, make sure you are in the root folder of your project
> npm install -g firebase-tools > firebase login > firebase init
The npm install is to get firebase tools installed on your system, the firebase login is for login in into your firebase account, while firebase init is for initializing firebase in the project.
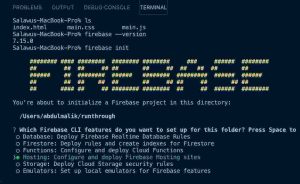
✅Scroll down to hosting and use your spaceBar button to pick it.
✅Click-use an existing project, since we’ve created the project In our console already
✅And you will see the project, just pick it
✅Now type public and enter
✅Press N and enter, we don’t want to override our index.html file.
don’t worry the setup are so simple, just pick default all the way through, and those settings can still be changed later, so don’t panic.
When done you will see a folder named public, .firebasesrc and files named firebase.json
now move all your HTML, CSS, JS, image files into that public folder and your code structure will look like this
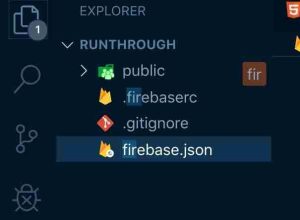
When you are done initializing firebase your workspace should look like this
So we are good to go, lets you deploy our code to firebase hosting using this command
> firebase deploy
and once the deploy is done successfully will see a response like this
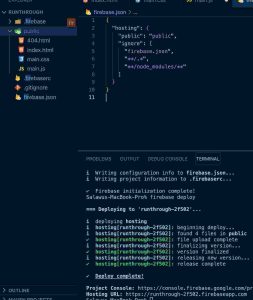
Goto your firebase console and click hosting and your dashboard should load up,
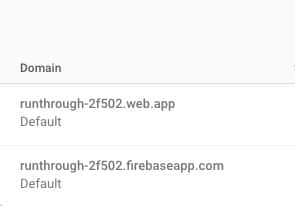
and you will see the two default firebase URL for your website, go to the link, where you see that your code is live and not just that alone the URL is having HTTPS meaning its a secure connection, automatic SSL Certificate on your site already.
So now its time to add the extra hosting addon
How to add a custom domain to your firebase project?
To add your own custom domain name click that adds Add custom domain and follow the setup by forwarding your domain name A, TXT, CNAME to firebase
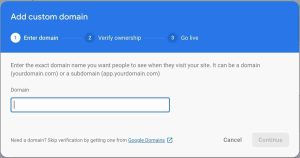
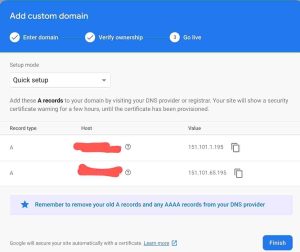
it simple just go to your domain registrar account and navigate to DNS option

and you see get the changes done
How to remove .html in the URL of your firebase project?

You want to build a web that has clean URLs, everyone too wanna do that, to remove .html in your web project just add this to your firebase.json file
"hosting": { // Add the "cleanUrls" attribute within "hosting" "cleanUrls": true }
How do you set up caching for your firebase project?
Its actually simple than you thought, for those of you that have used Apache Web Server, you will be familiar with .htaccess file where you get some caching, and site rules done and set, but in Firebase we have firebase.json file instead and here re the code sample to set cache to your website files.
"headers": [ {
"source": "**/*.@(js|css)",
"headers": [ {
"key": "Cache-Control",
"value": "max-age=300"
} ]
} ],
How do I redirect URLs on firebase project?
To redirect URLs or pages follow this pattern to get it done in your firebase.json file.
"redirects": [ { "source": "/foo", "destination": "/bar", "type": 301 }, { "source": "/firebase/**", "destination": "https://www.firebase.com", "type": 302 } ],
Looks like we will ending the Firebase hosting talk here🤗.
2# Firebase Realtime Database
RTDB was to enable web browsers to connect directly to the database with a realtime web socket connection, Browsers have made HTTP calls out to API services for years, but now, instead of making manual API calls, your browser could subscribe to the database directly and receive live updates.
The sad part is RTDB data structure is in pure JSON format, but we can shuffle this part with the Firestore
RTDB is meant for storing datasets that are not of large volume, so don’t send big volume data to RTDB, you can always use Cloud Firestore for big volume datasets.
😇We use the RTDB for streaming short-lived, constantly-changing data.
😇We use it for tracking logged-in users.
😇We use it for live progress notifications for long-running Cloud Functions.
😇But here we are going to create a form where people register and we get those data stored in RTDB.
Create a simple HTML file name is studentform. Nothing fancy, it’s just a level of seeing how things work.
Now copy your config file and paste it in your main.js file, your code should look like this, that’s how you can initialize firebase database, storage in your project
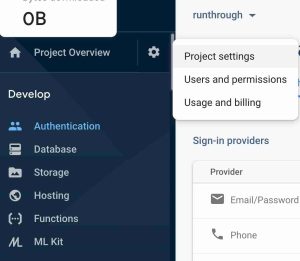
To find your config code, navigate to the project settings and you will find it there
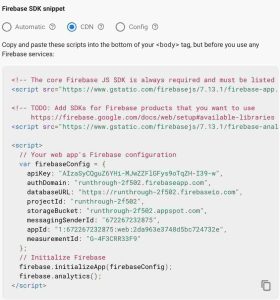
You’ve created the studentform.html file and pasted the firebase config into your main.js ?, now how do you store that information you receive in your form to your RTDB.
It’s simple, very few lines of code will get that done for us.
//Messages collection
var messagesRef = firebase.database().ref('studentdata');
// Listen for form submit
document.getElementById('registerForm').addEventListener('submit', submitForm);
// Submit form
function submitForm(e){ e.preventDefault();
// Get values
const name = getInputVal('name');
const department = getInputVal('department');
const faculty = getInputVal('faculty');
const year = getInputVal('email');
// Save message
saveMessage(name, department, faculty, email);
// Function to get get form values
function getInputVal(id){
return document.getElementById(id).value;
}
// Save message to firebase function
saveMessage(name, department, faculty, email){
var newMessageRef = messagesRef.push();
newMessageRef.set({
name: name,
department:department,
faculty:faculty,
email:email
}); }
our studentform.html snippet
<form id="registerForm"> <label for="name">Your Name</label> <input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Your Name" id="name" name="name" required data-error="Please enter your name"> <div class="form-group"> <label for="department">Department</label> <input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Your Department id="department" name="department" required data-error="Please enter your department"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="faculty">Faculty</label> <input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Your Faculty" id="faculty" name="faculty" required data-error="Please enter your faculty"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="faculty">Email</label> <input class="form-control" type="text" placeholder="Your mail" id="email" name="email" required data-error="Please enter your valid address"> </div> <div class="form-group"> <button type="submit" class="mt-4 btn btn-w3layouts btn-block btn-success text-white w-100 font-weight-bold text-uppercase">Confirm Registration</button> </form>
For us to store data from the form to our RTDB, we need to make the .write rule “true” and make the .read rule “false” in our RTDB Rules.
Now let’s talk about getting that solve and the security measures to be taken, so you won’t mess things up, you know security matters in Data collection.
Security In Firebase Realtime Database
The RTDB stores data in JSON, It’s security rules are also written in JSON and follow the pattern of the data that you plan on storing.
The starting JSON rules object is pretty simple:
{
"rules": {
".read": false,
".write": true
}
}
Notice that there’s a root attribute named rules and there are two kinds of permissions, .read and .write. There’s also an auth object available in the rule conditions which we can test to make sure that it’s not null. If it’s not null, then the request must be coming from an authenticated user!
Now let’s secure the user’s node on our JSON tree.
{
"studentform": {
"studentOne": {...},
"studentTwo": {...},
}
}
Yeah, we’re nesting our rules to match our data. So rules.users matches our user’s node in the JSON, you can also learn more on firebase docs.
3# Firebase Analytics
Firebase Analytics was added to the JavaScript SDK in version 7.0.0, make sure the firebase JS URLs in your project is up to date.
Adding Analytics to your web project can be done in two ways
1. Using the Firebase Default Analytics
Make sure you’ve added analytics in your firebase project console.
now move to your code and make sure you have the firebase config code in your main.js which contains measurementid field and calls firebase.analytics on initialization, see below
Collecting Data with Firebase Analytics
Firebase will collect data automatically for you since you’ve added the analytics package in your app bundle, but you might wanna see how users interact well on your web app, so you need to add some custom integration
Events
Events are critical to any good analytics dataset because they provide insight into how users interact with your app.
Google provides a variety of built-in events, but you can also create your custom events as shown below.
const analytics = firebase.analytics();
function onClickRead() {
// do something
analytics.logEvent('reading')
analytics.logEvent('reading', { chapter: '1' }) }
To see the custom reports click parameter reporting on firebase console then select the custom params
2. Using the default Google Analytics
This is the method I would recommend because it’s the best for the web since it was created mainly for the web.
So go create a Google Analytics account and set it up, you will be giving your tracking code which looks like this UA-XXXXXX-X
Now we need to create an analytics.js file in your project and paste the following snippet into the file
(function(i,s,o,g,r,a,m){i['GoogleAnalyticsObject']=r;i[r]=i[r]||function(){
(i[r].q=i[r].q||[]).push(arguments)},i[r].l=1*new Date();a=s.createElement(o),
m=s.getElementsByTagName(o)
[0];a.async=1;a.src=g;m.parentNode.insertBefore(a,m)
})(window,document,'script','https://www.google-analytics.com/analytics.js','ga');
ga('create', 'UA-XXXXXX-X', 'auto');
ga('send', 'pageview');
Replace the UA-XXXXXX-X with your tracking code and then link this analytics.js file into all your .html files, best practice for analytics is to add them in the head tags, you can also load it asynchronously to increase page speed.
I believe we’re done with Firebase Analytics also🤗.
4# Firebase Storage
Add the left sidebar In your firebase console, you will see a Develop that starts with authentication, Just click on storage and you should see something like this.
Cloud Storage can be used to upload images, videos, music any type of streaming or documents, the software you like, but whenever you reach the upload threshold for the Free Usage which is Spark Plan you will need to Upgrade depends on the Storage Level you need, Firebase isn’t costly.
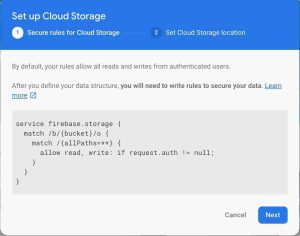
😎 Add a security rule for Firebase Storage, change that rule to below snippet JSON rule.
service firebase.storage {
match /b/{bucket}/o {
match /{allPaths=**} {
// Only Authenticated user can upload the file
allow read, write: if request.auth != null; // Anyone can upload the file/ No Auth Require
// allow read, write: true;
}
}
}
In this example, I have created a simple file input tag and add a JavaScript event onchange() with id files.
<input type="file" onchange="uploadFile()" id="files" name="files[]" multiple />
😎 Create a reference for Firebase Storage, In order to upload or download files, delete files, or get or update metadata, you must create a reference to the file you want to operate on.
A reference can be thought of as a pointer to a file in the cloud. References are lightweight, so you can create as many as you need, and they are also reusable for multiple operations.
😎 Create references from the storage() service in your Firebase app. This reference points to the root of your Cloud Storage bucket.
// Created a Storage Reference with root directory var storageRef = firebase.storage().ref();
Get the file from the DOM and create a reference to file
// Get the file from DOM
var file = document.getElementById("files").files[0];
console.log(file);
//dynamically set reference to the file name
var thisRef = storageRef.child(file.name);
Upload from a Blob or File Once you’ve created an appropriate reference, you then call the put() method. put() takes files from the JavaScript File and Blob APIs and uploads them to Cloud Storage.
//put request upload file to firebase
storagethisRef.put(file).then(function(snapshot) {
console.log('Uploaded a blob or file!');
});
and here is the Complete code:
<input type="file" onchange="uploadFile()" id="files" name="files[]" multiple />
<script>
//function to save file
function uploadFile(){
// Created a Storage Reference with root dir
var storageRef = firebase.storage().ref(); // Get the file from DOM
var file = document.getElementById("files").files[0];
console.log(file);
//dynamically set reference to the file name
var thisRef = storageRef.child(file.name);
//put request upload file to firebase storage
thisRef.put(file).then(function(snapshot) {
alert("File Uploaded")
console.log('Uploaded a blob or file!');
});
}
</script>
For a visual guide, check the below video.
5# Firebase Authentication
You can use Firebase Authentication to allow users to sign in to your web app using one or more sign-in methods, including email address and password sign-in, and federated identity providers such as Facebook, Google, Twitter
But in here I will only be covering for Authentication with Email and Password
1. Registration Of New User
Create a form that allows new users to register using their mail address and a password.
When a user completes the form, validate the email address and password provided by the user, then pass them to the regUserWithEmailAndPass() method:
<script>
var email="someone@example.com";
var password="password";
//Create User with Email and Password
firebase.auth().regUserWithEmailAndPass(email, password).catch(function(error) {
// Handle Errors Response.
var errorCode = error.code;
var errorMessage = error.message;
console.log(errorCode);
console.log(errorMessage);
});
</script>
2. Login Registered Users
Create a form page that allows registered users to sign in using their email address and password.
so whenever they fill in the correct details, call the loginWithEmailAndPass() method:
var email="runners@gmail.com";
var password="password";
//Login User with Email and Password
firebase.auth().loginWithEmailAndPass(email, password).catch(function(error) {
// Handle Errors Response Here.
var errorCode = error.code;
var errorMessage = error.message;
console.log(errorCode);
console.log(errorMessage);
});
</script>
3. Set an authentication state observer and get user data
For each of your app’s pages that need information about the signed-in user, attach an observer to the global authentication object.
This observer gets called whenever the user’s sign-in state changes.
Attach the observer using onAuthStateChanged() method. When a user successfully signs in, you can get information about the user in the observer.
firebase.auth().onAuthStateChanged(function(user) {
if (user) {
// User is signed in.
var displayName = user.displayName;
var email = user.email;
var emailVerified = user.emailVerified;
var photoURL = user.photoURL;
var isAnonymous = user.isAnonymous;
var uid = user.uid;
var providerData = user.providerData;
// ...
} else {
// User is signed out.
// ...
}
});
3. Login Out Users
To log out a user, call logOut():
firebase.auth().logOut().then(function() {
// Logged Out successful.
console.log('User Has Been Logged Out!');
}).catch(function(error) {
// Oops there's an error.
console.log(error);
});
5. Get Current Logged-In User Details
You can also get the currently logged-in user by using the currentUser property. If a user isn’t logged in, currentUser will be null:
var user = firebase.auth().currentUser;
if (user) {
// User is logged in.
if (user != null) {
name = user.displayName;
email = user.email;
photoUrl = user.photoURL;
emailVerified = user.emailVerified; uid = user.uid;
// The user's ID, unique to the Firebase project. Do NOT use
// this value to authenticate with your backend server, if
// you have one. Use User.getToken() instead.
}
} else {
// No user is logged in.
}
6. Update Registered User Details
You can update a user profile data, either the name, and some other data in their form using the updateProfile()method. For example:
var user = firebase.auth().currentUser;
user.updateProfile({
displayName: "Updated User's Name",
photoURL: "https://example.com/user/profile.jpg"
}).then(function() {
// Update successful.
console.log('User Profile Updated Successfully');
}).catch(function(error) {
// An error happened.
});
7. Set a user’s email address
You can set a user’s email address with the updateEmail() method. For example:
var user = firebase.auth().currentUser;user.updateEmail("user@example.com").then(function() {
// Update successful.
}).catch(function(error) {
// An error happened.
});.
8.Sending registered user a verification email
You can send also send verification email to a user with the sendEmailVerification() method.
var user = firebase.auth().currentUser;
user.sendEmailVerification().then(function() {
// Email sent.
}).catch(function(error) {
// An error happened.
});
9. Set a user’s password
You can set a user’s password with the updatePass() method.
var user = firebase.auth().currentUser;
var newPass = getASecureRandomPass();user.updatePass(newPass).then(function() {
// Password Update successful.
}).catch(function(error) {
// Oops an error occurred.
});
10. Send a password reset email to registered users
You can send a password reset email to a user with the sendPassResetEmail() method.
var auth = firebase.auth();
var emailAddress = "user@example.com";auth.sendPassResetEmail(emailAddress).then(function() {
// Email sent successfully.
console.log('Email Sent');
}).catch(function(error) {
// Oops an error occurred.
});
11.Delete Registered User
You can delete a user account with the delete() method.
var user = firebase.auth().currentUser;
user.delete().then(function() {
// User deleted successfully.
console.log('User Deleted');
}).catch(function(error) {
// Oops an error occurred.
});
You can also delete users from the Authentication section of the Firebase console, you can still further your knowledge on the documentation for Firebase Authentication For Web.
Question/Answer Time
I will love to answer a lot some already asked questions by my colleagues, so you all can also benefit
Can I host a CMS on Firebase?
Yes, you can in as much you have JavaScript Language in your box, then it will be easy for you, likewise you don’t have to stress your selves, I have done the research for you and here is the result.
The up and working platform that is readily made for Firebase CMS integration is Flamelink, but it’s a paid service, so imagine you doing a small project, you might not be able to afford to put the money on it🤷.
So I continued my research and I came across Eric Blog Project On GitHub, what he did was the implementation of CRUD, even though he never added the DeletePost Function, you feel free to make use of his code and likewise, you can contribute to improving the project, here is The Guide on how to build a CMS blog on Firebase The Guide on how to build a CMS blog on Firebase.
Can I host a WordPress Site On Firebase?
The answer is NO, Firebase is not a PHP based platform, so it won’t work.
Can I host Reactjs Project On Firebase?
Of course Yes, All JavaScript frameworks project can be hosted on Firebase, the likes of Vuejs, Angularjs, so here is How to deploy your Reactjs Website to Firebase.
So how did a noob like me get to know about firebase?
Yeah, I got to know about Firebase Technology through a kotlin meetup by the DSC Team at my University.
The Lead made mention of this sentence “I don’t buy a hosting plan, I use firebase to host my sites free” 😅
What !!! Free😳!!! My ear became more attentive, who don’t love free things 😂, then I got home and did more research on it.
The takeaway here is that you need to join a developer circle where ever you are, institution or state, you can join any of Circe be it Facebook Developer Circles, Google Developer Groups, Developer Student Clubs and you get to meet great people and learn new things.
Now It’s Your Turn
I hope this guide showed you how you can ease your developer activities and build great projects using Firebase.
Now I’d like to turn it over to you:
What’s the #1 Firebase Service from this post that you’re going to try?
Are you going to start using firebase hosting services? Or maybe you’re going to start using Firebase No SQL Database.
Or maybe you have a question about something related to firebase.
Either way, let me know by leaving a comment below right now.
Stay Safe✌️






Wow brother this was a really useful article. I hate the problem with finding the right host that wont fuck up all the time ro doesn’t have the right version of MySQL for example, so thank you for your great work will try this out next week, see if it fits my needs, I believe it does with just an cast of a blink of an eye.
am glad you found the guide helpfull
Wow brother this was a really useful article. I hate the problem with finding the right host that wont fuck up all the time ro doesn’t have the right version of MySQL for example, so thank you for your great work will try this out next week, see if it fits my needs, I believe it does with just an cast of a blink of an eye.
am glad you found the guide helpfull